Interstitial Velocity Dust Collector
Interstitial velocity dust collector. When sizing a pulse-jet dust collector it is important to consider not just air-to-cloth ratio but also interstitial velocity. This results in a high pressure drop and reduced efficiency of the filters. This can cause issues including.
Interstitial Velocity 3000 62 480 FPM Interstitial 18x Can Velocity. Upward velocity occurs when a hopper inlet is used on a pulse-jet baghouse. π of Bags.
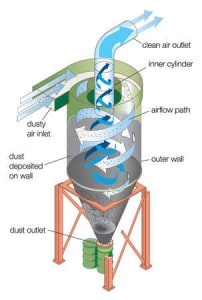
The interstitial velocity is the velocity of the unfiltered air traveling upward in between the bags. Interstitial Velocity FPM. To design a dust collector.
Sometimes the term can velocity is incorrectly used to refer to interstitial velocity. This velocity is greatest near the base of the bags before any air is absorbed through the media. The interstitial velocity is the upward velocity of air between the filters.
Enter ACFM of Air Side L in Side w in - Bag Dia2² π of Bags. The maximum interstitial velocity can be calculated by dividing the cfm filter capacity by the horizontal cross sectional area of the unit counting only the area outside of the bags. If the dust stays in suspension it will gravitate to the filters and ultimately penetrate and blind them over causing a high differential upset condition which can only be corrected by changing the filters.
Interstitial velocity is defined as the upward velocity of the air through the open area between the filter bags inside a dust collector. Interstitial velocity is the upward air velocity between the filters. One solution is to install pleated filter elements.
Interstitial Area 111 - 49 Sq Feet 62 Sq Feet. If the interstitial velocity is too high the dust pulsed off the bag will be re-entrained back into the bag instead of falling into the hopper for removal.
To design a dust collector.
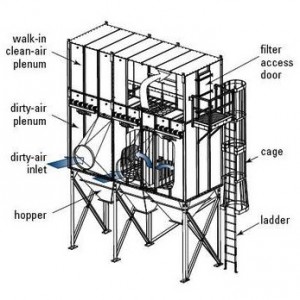
Collector Considerations Ł Air Velocity Œ Inlet Velocity Œ Can Velocity Œ Interstitial Velocity Œ Media Velocity 40fl 40fl Bag Bottom Area Qty p Radius 2 25 314 3fl 2 49 Sq Feet. Interstitial velocities that are too high greater than or equal to 250-300 FPM depending on the dust can cause high pressure drops. One solution is to install pleated filter elements. The maximum interstitial velocity can be calculated by dividing the cfm filter capacity by the horizontal cross sectional area of the unit counting only the area outside of the bags. Interstitial Velocity 3000 62 480 FPM Interstitial 18x Can Velocity. Interstitial velocity refers to the upward movement of air in the space between the filter bags in the dust collector. If the dust stays in suspension it will gravitate to the filters and ultimately penetrate and blind them over causing a high differential upset condition which can only be corrected by changing the filters. Instead the dust will be re-entrained back onto the bag surface. π of Bags.
Interstitial velocity is the upward air velocity between the filters. This results in a high pressure drop and reduced efficiency of the filters. Interstitial velocity is most critical when the dust being collected is light density. To design a dust collector. The can velocityalso called interstitial velocityor tank veloc- ity is the velocity of the upward airflow between the filters in the collector. Incomplete cleaning of the bag. Interstitial velocity is the upward air velocity between the filters.































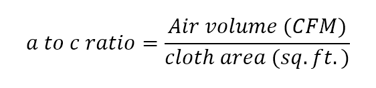
Posting Komentar untuk "Interstitial Velocity Dust Collector"